Exoplanet Caught on the Move
For the first time, astronomers have been able to directly follow the motion of an exoplanet as it moves from one side of its host star to the other.
The planet has the smallest orbit so far of all directly imaged exoplanets, lying almost as close to its parent star as Saturn is to the Sun. Scientists believe that it may have formed in a similar way to the giant planets in the Solar System.
Only 12 million years old, or less than three-thousandths of the age of the Sun, Beta Pictoris is 75% more massive than our parent star. It is located about 60 light-years away towards the constellation of Pictor (the Painter) and is one of the best-known examples of a star surrounded by a dusty debris disc. Earlier observations showed a warp of the disc, a secondary inclined disc and comets falling onto the star.
"Those were indirect, but tell-tale signs that strongly suggested the presence of a massive planet, and our new observations now definitively prove this," says team leader Anne-Marie Lagrange. "Because the star is so young, our results prove that giant planets can form in discs in time-spans as short as a few million years."
Recent observations have shown that discs around young stars disperse within a few million years, and that giant planet formation must occur faster than previously thought. Beta Pictoris is now clear proof that this is indeed possible.
The team used the NAOS-CONICA instrument (or NACO), mounted on one of the 8.2-metre Unit Telescopes of ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT), to study the immediate surroundings of Beta Pictoris in 2003, 2008 and 2009. In 2003 a faint source inside the disc was seen (eso0842), but it was not possible to exclude the remote possibility that it was a background star.
In new images taken in 2008 and spring 2009 the source had disappeared! The most recent observations, taken during autumn 2009, revealed the object on the other side of the disc after a period of hiding either behind or in front of the star (in which case it is hidden in the glare of the star).
This confirmed that the source indeed was an exoplanet and that it was orbiting its host star. It also provided insights into the size of its orbit around the star.
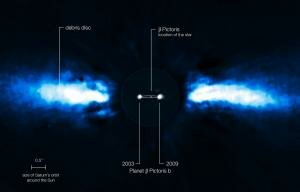
"The above annotated composite shows the reflected light on the dust disc in the outer part, as observed in 1996 with the ADONIS instrument on ESO's 3.6-metre telescope. In the central part, the observations obtained in 2003 and autumn 2009 with NACO of the planet are shown. The possible orbit of the planet is also indicated, albeit with the inclination angle exaggerated. (Credit: ESO/A.-M. Lagrange)"
Source: ESO
|